Crescent Sustainability Initiatives
Partnerships for the Goals (SDG 17)
SUSTAINABILITY LITERACY: TRANSFORMING DIGITAL AWARENESS INTO COMPREHENSIVE LEARNING
The Social Awareness Club (SAC) of B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, exemplifies a transformative approach to sustainability literacy, strategically addressing key dimensions of comprehensive environmental and social understanding. By leveraging digital platforms, the channel systematically develops critical competencies that align with the core principles of sustainability education, focusing on knowledge acquisition, critical thinking, and practical application of sustainable practices.
UNDERSTANDING SUSTAINABILITY THROUGH DIGITAL NARRATIVES
The YouTube channel (https://www.youtube.com/@SAC-CrescentCSE) demonstrates exceptional capability in breaking down complex sustainability concepts into accessible content. Each video serves as an educational tool that introduces fundamental sustainability principles, including sustainable development goals, ecological interconnectedness, and systemic environmental challenges. By presenting information through engaging narratives and practical demonstrations, the channel effectively transforms abstract concepts into comprehensible knowledge, enabling viewers to develop a nuanced understanding of sustainability beyond traditional academic frameworks.
CRITICAL THINKING AND SYSTEMS PERSPECTIVE
The channel’s content strategy goes beyond mere information dissemination, actively encouraging critical thinking and systems-based understanding. Videos exploring themes like natural food systems, agricultural practices, and consumption patterns challenge viewers to analyse interconnections between environmental, social, and economic systems. This approach cultivates a holistic perspective, enabling young audiences to recognize the complex relationships between individual actions and broader global sustainability challenges, thus developing essential critical analysis skills.
PRACTICAL SUSTAINABILITY LITERACY AND ETHICAL ENGAGEMENT
SAC-CrescentCSE distinguishes itself by bridging theoretical knowledge with practical implementation strategies. The videos provide actionable insights into sustainable practices, demonstrating how individuals can contribute to environmental conservation, responsible consumption, and community development. By highlighting local contexts and grassroots initiatives, the channel reinforces the ethical dimensions of sustainability, emphasising social responsibility, community empowerment, and intergenerational equity.
ASSESSMENT AND FUTURE LEARNING STRATEGIES
To enhance sustainability literacy, the channel could implement structured assessment mechanisms such as:
- Pre and post-viewing knowledge surveys
- Interactive comment section discussions
- Viewer challenge initiatives encouraging practical sustainability actions
- Collaborative project recommendations
- Reflective content that prompts personal sustainability commitments
These strategies would transform passive viewing into active learning, creating a comprehensive ecosystem of sustainability education that extends beyond digital platforms.
KEY LITERACY DEVELOPMENT COMPONENTS:
- Systematic knowledge transmission
- Critical thinking cultivation
- Practical skills development
- Ethical awareness enhancement
- Community engagement promotion
By integrating these elements, the SAC-Crescent CSE YouTube channel emerges as a pioneering model of digital sustainability literacy, demonstrating how technology can be leveraged to educate, inspire, and mobilize young change-makers committed to sustainable development.
Figure XVII (4.4) – 1 : YouTube – Social Awareness Club – Crescent CSE – Channel
SUSTAINABILITY LITERACY: TRANSFORMING STUDENT ENGAGEMENT THROUGH THE 17-DAY SDG CHALLENGE
The Social Awareness Club’s 17-day SDG Activity Challenge represents an innovative approach to enhancing sustainability literacy among students. It is meticulously designed to address key dimensions of comprehensive sustainability education. This initiative demonstrates a strategic method of transforming theoretical knowledge into practical, experiential learning that aligns perfectly with the core principles of sustainability literacy.
UNDERSTANDING SUSTAINABILITY THROUGH STRUCTURED ENGAGEMENT
The challenge systematically breaks down complex sustainability concepts by providing daily activities mapped to specific Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This approach directly addresses the fundamental requirement of understanding sustainability by:
- Introducing students to comprehensive SDG frameworks
- Providing context-specific learning experiences
- Encouraging active exploration of global sustainability challenges
- Creating opportunities for hands-on learning across different SDG domains
CRITICAL THINKING AND SYSTEMS PERSPECTIVE
The challenge’s design inherently promotes critical thinking and systems approach by:
- Requiring daily task completion and reflection
- Encouraging multiple submission formats (photos, artwork, videos, articles)
- Challenging students to connect individual actions with broader systemic impacts
- Facilitating a deeper understanding of interconnected sustainability challenges
ASSESSMENT AND LITERACY DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGY
The challenge incorporates multiple sustainability literacy assessment strategies:
- Pre and post-challenge knowledge evaluation
- Diverse submission formats demonstrating understanding
- Peer and expert review of submissions
- Performance-based recognition through prizes
- Documentation of learning journeys
KEY LITERACY DEVELOPMENT COMPONENTS:
- Structured SDG exploration
- Practical skill development
- Critical analysis encouragement
- Collaborative learning
- Experiential knowledge acquisition
INNOVATIVE LITERACY ENHANCEMENT STRATEGIES:
- Multi-modal learning approaches
- Gamification of sustainability education
- Peer-driven knowledge sharing
- Practical application of theoretical concepts
- Recognition and motivation mechanisms
ETHICAL AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY INTEGRATION
The challenge embeds ethical considerations by:
- Promoting responsible citizenship
- Encouraging community-oriented thinking
- Creating platforms for social impact
- Developing a sense of global interconnectedness
TECHNOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL LEARNING ECOSYSTEM
Leveraging digital platforms for challenge management:
- Google Classroom for submission tracking
- Online registration process
- Digital documentation
- Social media engagement
- YouTube channel content integration
INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT AND COLLABORATION
The challenge benefits from:
- Faculty mentorship
- Student leadership
- Institutional backing
- Clear communication channels
- Professional coordination
FUTURE LEARNING OBJECTIVES (2026)
- Develop comprehensive sustainability literacy benchmarks
- Create standardised assessment frameworks
- Expand challenge scope and participant engagement
- Establish long-term impact measurement strategies
The 17-day SDG Activity Challenge represents a holistic, innovative approach to sustainability literacy, transforming passive learning into active, engaged understanding. By providing structured, meaningful, and enjoyable learning experiences, the initiative demonstrates how educational institutions can effectively cultivate sustainability awareness and competence among young learners.

Figure XVII (4.4) – 3 : Social Awareness Club – 17 days SDG Activity Challenge
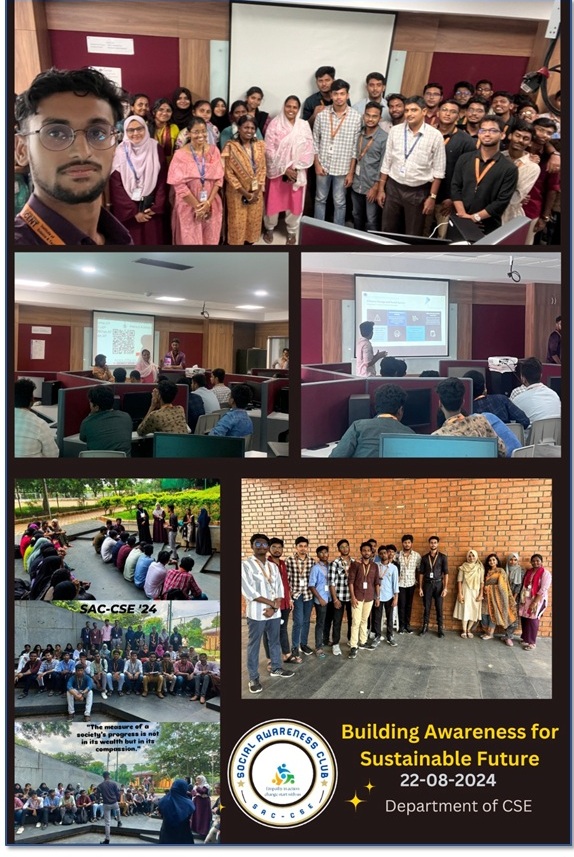

Figure XVII (4.4) – 4 : Building Awareness for Sustainable Future

Figure XVII (4.4) – 4 : Building Awareness for Sustainable Future – Brochure
SUSTAINABILITY LITERACY: ADVANCING RESEARCH AND INNOVATION THROUGH STRATEGIC COLLABORATION – CGOM
The landmark Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between Crescent Global Outreach Mission R&D and NanoFold Inc. represents a sophisticated model of sustainability literacy development. It demonstrates how institutional collaborations can transform educational and research paradigms while addressing critical global challenges.
UNDERSTANDING SUSTAINABILITY THROUGH INTERDISCIPLINARY RESEARCH
The collaborative project embodies comprehensive sustainability literacy by:
- Integrating multiple scientific disciplines
- Addressing critical global challenges in sustainable materials and energy storage
- Connecting academic research with real-world industrial requirements
- Providing practical context to theoretical sustainability concepts
KEY SUSTAINABILITY LITERACY DIMENSIONS
- Systems Thinking
- Demonstrates interconnectedness of materials science, energy technology, and sustainable development
- Illustrates complex relationships between technological innovation and environmental solutions
- Showcases how different scientific domains collaborate to address holistic challenges
2. Critical Analysis and Problem-Solving
- Develops research frameworks targeting sustainable building materials
- Explores innovative energy storage solutions
- Encourages analytical thinking beyond traditional disciplinary boundaries
- Promotes solution-oriented approach to global sustainability challenges
3. Practical Skill Development
- Provides hands-on research experience
- Enables faculty and student engagement in cutting-edge projects
- Creates opportunities for practical application of theoretical knowledge
- Develops technical competencies aligned with sustainable development goals
ASSESSMENT AND LITERACY MEASUREMENT STRATEGIES
- Research Output Evaluation
- Tracking project milestones and deliverables
- Assessing technological innovations generated
- Monitoring potential market and environmental impacts
- Documenting knowledge transfer and skill acquisition
2. Collaborative Learning Mechanisms<
- Interdepartmental knowledge exchange
- Industry-academia partnership model
- Exposure to real-world research challenges
- Mentorship from experienced researchers
ETHICAL AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY COMPONENTS
- Alignment with national sustainable development goals
- Potential for transformative technological solutions
- Addressing global challenges in construction and energy
- Promoting responsible innovation
Table XVII (4.4) – 1: sustainability literacy development framework
Dimensions | Strategies | Outcomes |
Conceptual Understanding | Interdisciplinary Research | Comprehensive Sustainability Insights |
Practical Skills | Industry Collaboration | Innovative Technological Solutions |
Ethical Awareness | Social Impact Assessment | Responsible Innovation |
Critical Thinking | Complex Problem Solving | Adaptive Research Approaches |
FUTURE LEARNING AND RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
- Establish sustainable research collaboration models
- Create transferable knowledge frameworks
- Develop industry-relevant curriculum
- Foster continuous innovation ecosystem
INSTITUTIONAL IMPACT
- Positioning as a leader in sustainable research
- Inspiring future scientific innovators
- Contributing to the national sustainable development agenda
- Creating knowledge pathways for complex global challenges
The CGOM-NanoFold collaboration exemplifies an advanced approach to sustainability literacy. It transforms traditional educational boundaries by creating dynamic, interdisciplinary learning environments that prepare students to address complex global challenges through innovative research and technological solutions.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Integrated approach to sustainability education
- Practical research-based learning
- Interdisciplinary collaboration
- Real-world problem-solving
- Ethical technological innovation

Figure XVII (4.4) – 4 : Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between Crescent Global Outreach Mission R&D and Nano Fold Inc.


