Crescent Sustainability Initiatives
Partnerships for the Goals (SDG 17)

Advancing Sustainability: A Comprehensive Report on the B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology’s Commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals
A. Advancing Sustainable Development Goals at B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology
Commitment to Sustainability and the SDGs
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology has demonstrated a robust commitment to sustainability and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through extensive partnerships with regional NGOs and government entities. These collaborations enable the university to contribute directly to the development and implementation of SDG-focused policies and initiatives at both local and national levels.
Diverse Partnerships Addressing Sustainability Challenges
The university’s partnerships span a wide range of organizations, each contributing unique expertise and resources. For example, collaboration with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) – Central Leather Research Institute (CLRI) focuses on innovative biogas technologies to tackle energy and waste management challenges, aligning with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). Additionally, engagement with the State Level Solid Waste Management Committee allows the university to provide industry-level insights for improving waste management systems, contributing to SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 12.
Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development
The university’s collaborations with organizations such as Aloe Ecell, Cambridge Cleantech, and the Israeli National Center of Blue Economy reflect a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of environmental sustainability, technology, and regional development. These partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange, pilot innovative solutions, and co-create strategies that address complex challenges related to water management, renewable energy, and sustainable industries—all crucial for achieving the SDGs.
Engaging in Cross-Sectoral Dialogue for Sustainable Development
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute actively fosters cross-sectoral dialogue about the SDGs through various initiatives, including the 6th International Conference on Management, Accounting, Banking, Economics, and Business Research for Sustainable Development held on March 1st and 2nd, 2023. This conference served as a vital platform for academia, industry professionals, and policymakers to discuss pressing issues related to sustainable development.
Integrating Sustainability into Business Practices
During the conference, participants engaged in discussions emphasizing the integration of sustainable development principles into business practices. Notable speakers highlighted how entrepreneurship can drive social and environmental sustainability, showcasing the potential for academic and professional communities to contribute valuable insights to SDG policy formulation.
Building a Collaborative Framework for Future Initiatives
The successful execution of the conference laid the groundwork for ongoing relationships between academia, government, and NGOs. By engaging in meaningful discussions and sharing research findings, participants contributed to a collective understanding of the challenges and opportunities related to the SDGs. Moving forward, maintaining open lines of communication among stakeholders will enhance the effectiveness of policies that foster a low-carbon economy and achieve sustainable development.
Fostering International Collaboration for Sustainable Development Goals
The Crescent Institute is committed to international collaboration to advance the SDGs. On May 17, 2023, a significant meeting was organized with Mr. Hiroaki Yumoto, Chairman of the International SDGs Human Resource Support Association from Osaka, to explore collaborative opportunities with Japanese institutions. This cooperation aims to enhance cross-cultural learning experiences and promote knowledge sharing.
Enhancing Sustainable Development through International Internships
The Centre for International Relations (CIR) hosted a meeting focused on international internships related to sustainability projects. This initiative aligns with the university’s commitment to sustainable development by fostering direct involvement in policy development related to the SDGs. Students are provided opportunities to engage in hands-on experiences, enhancing their understanding of adaptive management practices.
Integrating Sustainability into the Academic Curriculum
The integration of sustainability into the academic curriculum is pivotal in fostering a culture of awareness and action among students. The B.Arch and B.Des programs include dedicated sustainability courses, ensuring that students are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to tackle contemporary environmental challenges. Furthermore, the curriculum incorporates SDGs into the Programme Educational Objectives (PEOs), reinforcing the importance of sustainable practices in architectural education.
Fostering Knowledge Exchange and Collaboration
The institution actively facilitates platforms for knowledge exchange through events such as international conferences and expert-led workshops. Recent conferences have brought together architects and experts globally to discuss sustainable practices in architecture. Regular engagement with industry experts during curriculum reviews ensures that academic programs remain relevant and responsive to emerging trends.
Research-Driven Solutions: Evaluating and Enhancing Practices
The Crescent Innovation and Incubation Council (CIIC) plays a crucial role in fostering collaboration for best practices in achieving the SDGs. CIIC hosts over 130 start-ups across various sectors and employs a Triple ‘M’ Strategy—Mentor, Money, and Market—to empower entrepreneurs to develop innovative solutions aligned with the SDGs. This strategic approach enhances individual start-up capacities and strengthens the broader societal impact of innovative solutions.
Showcasing Achievements through EDGE Certification
The institute’s commitment to sustainability is further exemplified through its green building projects, certified under the EDGE program. These projects showcase significant energy and water savings, reflecting the university’s dedication to creating a sustainable living and learning environment. The successful implementation of eco-friendly construction practices, such as the use of low-VOC paints and recycled materials, contributes to a smaller environmental footprint.
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology exemplifies a proactive approach to advancing the Sustainable Development Goals through diverse partnerships, international collaboration, and a commitment to integrating sustainability into education and research. By fostering a culture of innovation and sustainability, the institute is paving the way for impactful solutions that contribute meaningfully to global challenges, reinforcing its dedication to the SDGs.
B. Enhancing Sustainability Literacy at B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology is at the forefront of promoting sustainability literacy through innovative educational initiatives. By integrating sustainability principles into its curriculum and leveraging digital platforms, the institute is equipping students with the knowledge and skills necessary to address pressing global challenges. This comprehensive approach encompasses various programs, including the Social Awareness Club (SAC), the 17-day SDG Activity Challenge, and strategic collaborations with industry partners.
Sustainability Literacy through Digital Platforms
The Role of the Social Awareness Club
The Social Awareness Club (SAC) of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering exemplifies a transformative approach to sustainability literacy. Through its YouTube channel, SAC-CrescentCSE, the club breaks down complex sustainability concepts into accessible content. Each video serves as an educational tool, introducing fundamental principles such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), ecological interconnectedness, and systemic environmental challenges. By presenting information through engaging narratives and practical demonstrations, the channel enables viewers to develop a nuanced understanding of sustainability beyond traditional academic frameworks.
Critical Thinking and Practical Application
The content strategy of the SAC-CrescentCSE channel actively encourages critical thinking and a systems-based understanding of sustainability. Videos exploring themes like natural food systems and consumption patterns challenge viewers to analyze the interconnections between environmental, social, and economic systems. This holistic perspective cultivates essential critical analysis skills, enabling young audiences to recognize the complex relationships between individual actions and broader global sustainability challenges.
Moreover, the channel bridges theoretical knowledge with practical implementation strategies, providing actionable insights into sustainable practices. By highlighting local contexts and grassroots initiatives, it reinforces the ethical dimensions of sustainability, emphasizing social responsibility and community empowerment.
The 17-Day SDG Activity Challenge
Structured Engagement for Sustainability Literacy
The 17-day SDG Activity Challenge represents an innovative approach to enhancing sustainability literacy among students. This initiative systematically breaks down complex sustainability concepts by providing daily activities mapped to specific SDGs. Students are introduced to comprehensive SDG frameworks, context-specific learning experiences, and opportunities for hands-on learning across different domains.
The challenge promotes critical thinking and a systems approach by requiring daily task completion and reflection. Students are encouraged to submit their work in various formats—photos, artwork, videos, and articles—challenging them to connect individual actions with broader systemic impacts. This multifaceted engagement facilitates a deeper understanding of interconnected sustainability challenges.
Assessment and Future Learning Strategies
To enhance sustainability literacy, the challenge incorporates multiple assessment strategies, including pre and post-challenge evaluations, peer reviews, and performance-based recognition. By transforming passive viewing into active learning, the initiative creates a comprehensive ecosystem of sustainability education that extends beyond digital platforms.
Advancing Research and Innovation through Strategic Collaboration
The CGOM-NanoFold Collaboration
The partnership between Crescent Global Outreach Mission (CGOM) and NanoFold Inc. exemplifies how institutional collaborations can transform educational and research paradigms while addressing critical global challenges. This collaborative project integrates multiple scientific disciplines to tackle issues related to sustainable materials and energy storage.
By connecting academic research with real-world industrial requirements, the collaboration provides practical context to theoretical sustainability concepts. It fosters systems thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving skills, enabling students and faculty to engage in cutting-edge projects that align with sustainable development goals.
Ethical and Social Responsibility
The CGOM-NanoFold collaboration emphasizes ethical and social responsibility by aligning with national sustainable development goals and promoting responsible innovation. This partnership not only positions the institute as a leader in sustainable research but also inspires future scientific innovators to contribute to the national sustainable development agenda.
Curriculum Integration for Sustainable Development
Commitment to Meaningful Education
The integration of sustainability-focused courses across diverse academic disciplines is vital for preparing a generation capable of meeting the challenges posed by the SDGs. The civil engineering department, for instance, offers courses like “Environmental Studies” and “Water and Wastewater Engineering,” which are aligned with SDG 6, emphasizing clean water and sanitation.
Courses such as “Social Entrepreneurship” within the management studies framework contribute significantly to achieving SDG 8, focusing on decent work and economic growth. By empowering students to create sustainable business models, these courses foster economic empowerment and social change.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary courses like “Green Design and Sustainability” and “Smart Cities” emphasize the collaborative nature of addressing sustainability challenges. By encouraging students from various departments to work together, these programs foster a culture of sustainability across the institution, preparing future professionals to approach environmental, social, and technological challenges holistically.
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology is making significant strides in enhancing sustainability literacy through innovative educational initiatives, digital engagement, and strategic collaborations. By integrating sustainability principles into its curriculum and fostering critical thinking, practical application, and ethical awareness, the institute is preparing students to become empowered individuals ready to make meaningful contributions to their communities and the world at large. Through these efforts, the institute is not only advancing its educational mission but also playing a crucial role in addressing global sustainability challenges.
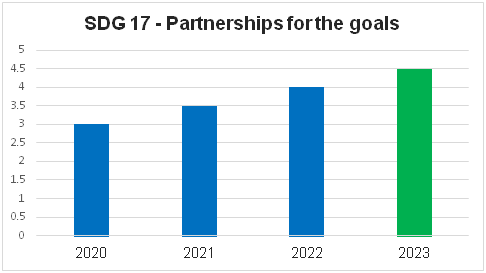
SDG17: Partnerships for the goals
| 4 to 5 | There is significant progress in effective implementation compared to the previous year |
| 3 to 4 | The necessary processes/activities (Relationships with regional NGOs and government for SDG policy, Publication of SDG reports, Education for the SDGs) have been implemented |
| 2 to 3 | There is an explicit plan to address the ‘Partnerships for the goals’ and necessitated processes have been initiated |
| 1 to 2 | There is an understanding and willingness to contribute effectively for achieving the UN targets of SDG 17 |
| 0 to 1 | There is no/partial willingness and plan to contribute for achieving the UN targets of SDG 17 Partnerships for the goals |

Please find the Report: SDG ACCORD REPORT


