
Innovating for resilient infrastructure
A.INDUSTRY, INNOVATION AND INFRASTRUCTURE
B.S.Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Technology has established an Technology Based Incubator “Crescent Innovation and Incubation Council (CIIC)” at a sprawling 25000+ sq. ft of space for an immediate jumpstart on September 2018. CIIC was incorporated as a separate legal entity i.e. ‘Section-8 not for profit company’ on March 2019 as per the government norms for Incubation Centres.
Since its inception, CIIC has strived to be at the forefront in the incubation arena. providing state-of-the-art facilities and high throughput technologies in the area of Industry 4.0, Life Sciences & Mobility and Transportation by establishing Centre of Excellence (CoE). These CoE’s supports with cutting edge techniques and technologies to start-ups& business coaching and mentoring to ambitious entrepreneurs. Networking with professionals from industries and academia, gain backing from the corporate and investors are the few core strengths of CIIC for their start-ups to venture to ensuing phase of their businesses.
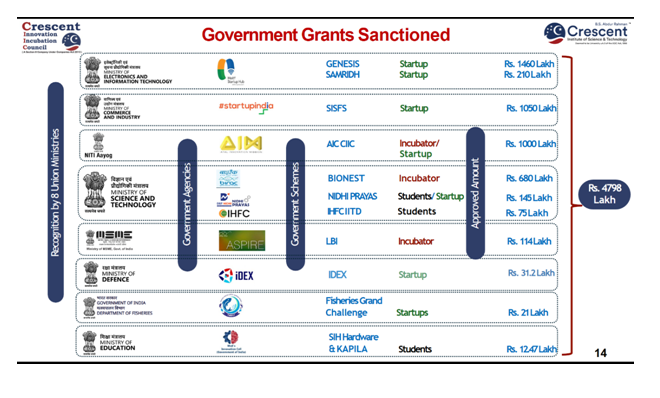
The main objective is to convert more students into entrepreneurs and at the same time facilitate ideation stage start-ups in the ecosystem to accelerate them to the growth stage at a rapid pace. Our thrust areas are Life Sciences, Industry 4.0 and Mobility Transportation which are also the core economic sectors for the state of Tamil Nadu. We have received various Government grants from BIRAC, SISFS, EDII and GITA.
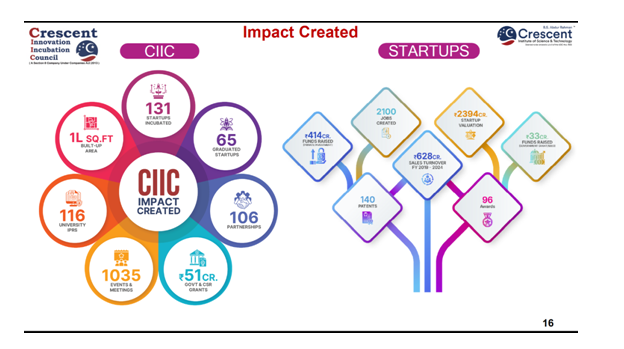
CIIC has currently incubated 200+ start-ups and has been acting as a “One Stop Shop – Technology Business Incubator (TBI)” for start-ups in the field of Life Sciences, Industry 4.0 and Mobility and Transportation.
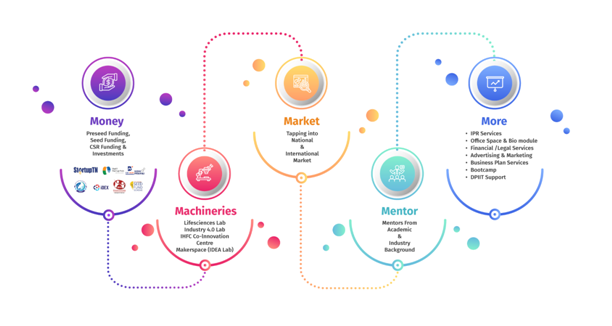
CIIC aims to support & render start-up into a profitable entity through the mission statement called Triple ‘M’ – Market, Money and Mentor transforming innovation into scalable business models with high productive impact, encouraging interdisciplinary advancement both nationally and internationally.
CIIC is recognized by the European Commission for collaborative projects and soft landing of startups. CIIC is administered by 10+ full time team with industry background to support startups.
B. Advancing Economic Growth through Innovation
CIIC aligns with SDG 9 by creating an ecosystem where innovation thrives. By nurturing these startups, the center promotes economic growth that prioritizes sustainability, ultimately enhancing community resilience. The focus on innovative solutions is crucial for addressing pressing social and environmental issues, ensuring that economic advancements do not come at the expense of our planet.
In conclusion, CIIC’s commitment to fostering innovative and sustainable industrial practices is pivotal for advancing SDG 9. By empowering startups and promoting resilience, the center plays an essential role in shaping a sustainable future, fostering economic growth, and building a more innovative society.


D. Evaluating University Research Impact: Patents Citing B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology
B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology (BSACIST) demonstrates a strong commitment to research and innovation, as evidenced by its growing portfolio of patents citing its research.
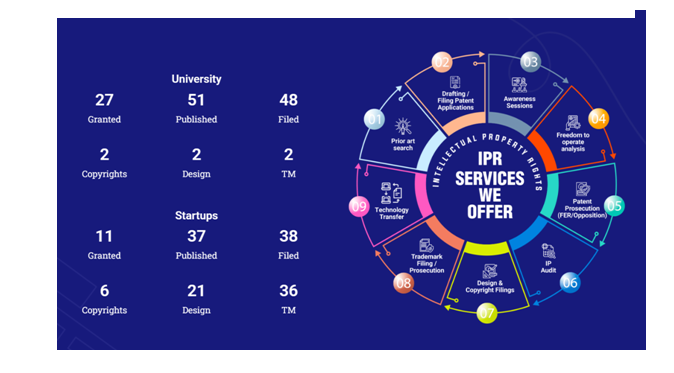
Notable innovations include advancements in recycling technologies and synthesis methods that reflect significant contributions to various fields, indicating the relevance of university research to both industry and society.
In addition to the number of patents cited, the institute prides itself on fostering an environment conducive to innovation, evident in the number of granted patents, which totalled four over the same period. This emphasis on research not only enhances the institution’s academic reputation but also highlights the importance of university-led innovations in addressing contemporary challenges. By linking research outcomes to industry applications, BSACIST underscores its role in contributing to Sustainable Development Goal 9 (SDG 9), which focuses on building resilient infrastructure and promoting sustainable industrialization for a more innovative future.
Patent Grant Recognition for Innovative Research at BSACIST

The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology (BSACIST) has recently achieved a significant milestone in innovation with the granting of a patent for its research entitled “Synergistic Gas Nanoemulsion Compositions and Methods of Synthesis Thereof.” This patent, numbered 407699, reflects the institution’s commitment to advancing scientific knowledge and practical applications in emerging technologies.
Filed on September 15, 2021, the patent has been granted for the term of 20 years, showcasing the long-term value of the research conducted at BSACIST. This innovative work contributes to the fields of nanotechnology and emulsion science, presenting potential implications for various industrial applications, including energy solutions and environmental sustainability.
By securing this patent, BSACIST not only strengthens its academic and research reputation but also enhances its collaboration opportunities with industry partners eager to leverage cutting-edge technologies. This recognition is emblematic of the institute’s strategic focus on producing research that is not only academically rigorous but also commercially relevant, thereby bridging the gap between academia and industry.
The patent serves as a testament to the quality and impact of research conducted at BSACIST, contributing significantly to the university’s vision of fostering innovation that meets the needs of society and industry alike. It positions the institution as a key player in the development of sustainable technologies, which is essential for addressing the pressing challenges of today’s world.

Patent Certificate for Innovative Research at BSACIST
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology (BSACIST) has achieved a noteworthy milestone by being granted a patent for an innovative research project entitled “Method for the Synthesis of Graphene Oxide Incorporated Copper Bismuth Nanorods.” This patent, numbered 440391, was filed on April 10, 2021, under Application No. 2021411018915.
Key Details of the Patent
• Inventors: The research was led by Dr. Mohd Ashfaq along with collaborators Neetu Talreja and Divya Chauhan, showcasing a strong collaborative effort in advancing scientific inquiry at the institute.
• Date of Grant: This patent was officially granted on July 25, 2023, marking a significant recognition of the research’s novelty and potential applications.
• Duration: The patent is valid for a term of 20 years from the date of filing, providing a robust framework for the protection of intellectual property.

Significance of the Research
The research focuses on synthesizing advanced materials—specifically, copper bismuth nanorods incorporated with graphene oxide. The significance of such materials lies in their potential applications across various industries, including electronics, medical devices, and energy solutions. By developing efficient synthesis methods, this research contributes to the growing field of nanotechnology, enabling the creation of innovative solutions tailored for modern challenges.
Contribution to Innovation Ecosystem
This patent not only strengthens BSACIST’s position as a leader in cutting-edge research but also reflects the institution’s commitment to fostering innovation that aligns with global technological advancements. The success of this patent paves the way for further research endeavors, supports the establishment of a vibrant startup ecosystem, and contributes to India’s mission of self-reliance in technology—aligned with the “Atma Nirbhar Bharat Mission.”
In summary, the granting of this patent is a testament to the high-quality research and development efforts at BSACIST. It highlights the institution’s role in producing viable, market-ready innovations while encouraging young researchers to pursue groundbreaking scientific inquiries.
A. Synergistic Composition for Inhibiting Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete Structures
Overview
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology (BSACIST) has officially been granted a patent for its innovative solution aimed at combating corrosion in reinforced concrete structures. This development addresses a critical challenge in civil engineering, directly impacting the longevity and safety of infrastructure.
Importance of the Invention
Inhibiting corrosion is crucial for maintaining the integrity and durability of concrete structures, which are essential in various construction projects. The patented composition is designed to enhance the performance of reinforced concrete, thereby contributing to more sustainable and resilient building practices. The innovation is set to make a significant difference in the construction industry, aligning with current trends towards long-lasting and environmentally friendly construction materials.
Intellectual Property Impact
This patent underscores BSACIST’s commitment to advancing research and innovation in material sciences. The granted patent is protected for a term of 20 years from the filing date, ensuring the institute retains exclusive rights to this significant technological advancement. Such initiatives enhance the institution’s role as a leader in innovative research and development, fostering a culture of entrepreneurship and innovation.
In conclusion, the granted patent demonstrates BSACIST’s dedication to addressing real-world challenges through scientific inquiry, paving the way for further advancements in the realm of construction and material technology. This achievement not only reinforces the institute’s reputation but also supports the broader goal of enhancing infrastructure resilience and sustainability.

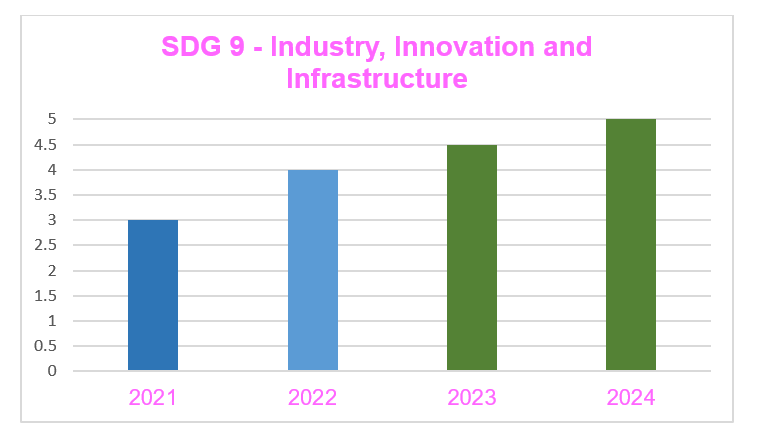
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
| 4 to 5 | There is significant progress in effective implementation compared to the previous year |
| 3 to 4 | The necessary processes/activities (University spin offs, Research income from industry and commerce) have been implemented |
| 2 to 3 | There is an explicit plan to address the ‘Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure’ and necessitated processes have been initiated |
| 1 to 2 | There is an understanding and willingness to contribute effectively for achieving the UN targets of SDG 9 |
| 0 to 1 | There is no/partial willingness and plan to contribute for achieving the UN targets of SDG 9 Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
SDG ACCORD REPORT 2025
B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology (BSACIST), this positions the institute not only as a learner but as a contributor to national and regional SDG policy dialogues. The 2024 entry on relationships with regional NGOs and government for SDG policy underscores an ongoing posture of engagement with policy ecosystems, aligning institutional activity with policy development, monitoring, and adaptive management. This alignment suggests BSACIST can translate its SDG work into formal policy input, scenario modelling, and accountability mechanisms
that inform broader regional development trajectories.
The 2025 SDG Accord report highlights that most signatories are moving toward embedding sustainability at an organizational level, with many reporting up-to-date sustainability policies endorsed by senior leadership. For BSACIST, the implication is to articulate a clear, leadership-backed sustainability policy or action plan that directly references SDGs most relevant to the institute’s mission and operations. Given the 2024 emphasis on engaging with government and regional NGOs, BSACIST could position its policy inputs as anchored in the connected governance and partnerships depicted in the report, ensuring that policy submissions, stakeholder consultations, and adaptive management are institutionally codified rather than ad hoc activities.
The SDG Accord Progress Report 2025 frames universities and colleges as pivotal agents for implementing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals through whole-institution approaches. The thematic focus on Learning and Teaching reveals that while progress is ongoing, Learning and Teaching remains the least mature operational area for many signatories. BSACIST should view this as a guide to invest in curriculum integration of SDGs, faculty development, and assessment practices that explicitly test sustainability knowledge. The report notes significant barriers such as limited time for staff development and inadequate integration of sustainability into curricula. BSACIST can address these barriers by allocating dedicated funding and time for professional development, integrating SDG-related outcomes into degree programs, and creating standardized assessments that measure students’ sustainability competencies.
The progress report emphasizes the value of evidence-based case studies and peer learning. BSACIST can contribute through documenting and sharing successful Learning and Teaching innovations—for example, climate pedagogy initiatives, service-learning projects, and interdisciplinary modules that map to SDG4 (Quality Education), SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG17 (Partnerships for the Goals). By contributing BSACIST-specific case studies to the SDG Accord platform, the institute would participate in a global knowledge network, enabling replication and contextual adaptation across similar universities and colleges in the region.
The results section of the report highlights top SDGs influenced by signatories and the priority SDGs for the upcoming year. In the last year, SDG4, SDG13, and SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) were prominent, with SDG17 as a top priority for partnerships. For BSACIST, this pattern suggests focusing efforts on education quality, climate action initiatives, and strengthening collaborative frameworks with industry, government bodies, and civil society. Establishing formal partnerships and joint programmes with regional NGOs and the government can advance SDG implementation while creating opportunities for funding, capacity-building, and scalable impacts.
The report documents the internal and external support needs identified by signatories, with budget, dedicated staff capacity, and funding from external sources highlighted as top needs. BSACIST should prepare a resource plan that secures funding streams for SDG-aligned activities, including staff training, climate-related research, and curriculum transformation. Engaging government and sector partners can help unlock external support, align institutional priorities with national development plans, and provide procurement or grant-based pathways to sustain SDG initiatives over multiple years.
Finally, the BSACIST context benefits from the report’s emphasis on evaluating new partnerships and governance improvements. The Accord notes that sustainability work benefits from cross-departmental collaboration and a shared, mission-driven culture. BSACIST can leverage its 2024 policy-involvement experience to foster cross-disciplinary governance structures, establish an SDG steering committee, and implement a transparent reporting framework that communicates progress to internal and external stakeholders. By aligning these governance practices with the SDG Accord methodology, the institute can demonstrate measurable progress toward embedding the SDGs into education, research, operations, and community engagement.



