
“Advancing Climate Action”
Climate change is a crisis that will affect every part of society, and every country. Universities need to be at the forefront of action to reduce the impact of climate change, especially amongst the poorest who will be the most affected.
B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology is actively tackling climate change through a integrated strategy that combines research, education, and the deployment of low-carbon energy solutions. Acknowledging the uneven effects of climate change on vulnerable populations, the institute is dedicated to lowering its carbon footprint and embedding sustainable practices across campus. A key milestone in its sustainability agenda is the deployment of rooftop solar PV installations totaling 650 kWp, designed for captive consumption and capable of offsetting about 474 metric tons of CO2 annually—roughly equivalent to the carbon sequestration of 21,545 trees. This not only advances carbon neutrality but also supports SDG 7 by promoting affordable, clean energy. Beyond renewables, BSACIST conducts thorough carbon footprint assessments and environmental education. It hosts a Continuous Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Station (CAAQMS) in partnership with the Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board, reflecting a strong commitment to air quality improvement. The institute also cultivates sustainability awareness through events like the Indian Social Science Congress, which brings together interdisciplinary dialogues on environment, energy, and health. Collectively, these efforts position BSACIST as a model for other institutions, demonstrating a sustained commitment to reducing emissions, expanding renewable energy, and engaging the campus community in environmental stewardship for a greener future.
Carbon Neutrality at BSACIST: A Comprehensive Approach to Sustainable Campus Management
Benchmarking Carbon Efficiency:
Redefining Institutional Environmental Performance B. S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology (BSACIST) has implemented a comprehensive carbon management strategy that significantly reduces its carbon footprint through innovative and sustainable practices. The institute’s total carbon emission stands at 7,369 tons per year, with a per capita carbon footprint of 1.05 tons, which is remarkably lower than the national average of 1.58 tons per capita. This represents a 33.54% reduction from the national average, demonstrating the institution’s commitment to environmental sustainability and carbon reduction.
Green Infrastructure – Strategic carbon offsetting through Ecological Interventions:
The carbon offsetting strategy at BSACIST is multifaceted, leveraging green areas and renewable energy initiatives to mitigate carbon emissions. The campus boasts 19 acres of green spaces, including tree-covered areas, lawns, and Beema Bamboo plantations, which collectively absorb 747 tons of CO2 annually. This represents 10.13% of the total carbon emissions, with the green areas covering 37.86% of the campus. The solar infrastructure plays a crucial role in this carbon reduction effort, with 650 kWp of solar photovoltaic plants installed across campus buildings, offsetting approximately 474 tons of CO2 emissions annually – equivalent to planting 21,545 trees.
Green Areas – 19 Acres (37.86% of the Total Campus)

Holistic Emission Management : Integrated Technological and Operational Strategies
The institute’s carbon management approach extends beyond green spaces and solar energy. The comprehensive strategy includes multiple energy-efficient technologies and sustainable practices across various campus operations. Transportation emissions are carefully managed, with detailed tracking of petrol and diesel consumption. Electricity consumption, which accounts for the largest portion of carbon emissions (5,251,791 kg CO2), is being systematically reduced through energy-efficient technologies, including high-performance building envelopes, efficient lighting systems, and advanced HVAC technologies. The institute has also implemented water conservation measures and waste management strategies that contribute to overall carbon reduction.
Innovative Technologies and Collaborative Sustainability : Beyond Traditional Approaches
Innovative technologies and collaborative approaches further enhance BSACIST’s carbon management efforts. The implementation of zero-export devices for solar power management, solar water heating systems, and energy-efficient building designs demonstrate a holistic approach to sustainability. The solar water heating systems, with a total capacity of 39,500 litres, are estimated to save approximately 24 lakhs in power consumption annually. Additionally, student-driven projects, such as solar street lighting installations, showcase the institute’s commitment to engaging the academic community in sustainable practices.
Driving Sustainability: The Role of Eco-Friendly Vehicles in BSACIST’s Green Transportation Initiative
The integration of eco-friendly vehicles into the university’s transportation system highlights a practical application of BSACIST’s sustainability values, encouraging a shift toward cleaner mobility solutions while reducing overall campus emissions.

CARBON FOOTPRINT
| Carbon foot print / Capita | ||||||
| Activity Data | Type | unit | GHG | Emission factor | Quantity | CO2 emission / year |
| Transportation | petrol | litres | KgCO2e | 2.196 | 1300 | 2855 |
| diesel | litres | 2.65 | 381461 | 1010872 | ||
| Electricity | kWh | KgCO2e | 1.2 | 4376492 | 5251791 | |
| Paper consumption | kg | KgCO2e | 0.683 | 21900 | 14958 | |
| Water consumption | water supply | cum | KgCO2e | 0.8 | 160611 | 128489 |
| Solid waste | kg | KgCO2e | 3.7 | 259560 | 960372 | |
| Total CO2 Emission Per Year | Kg | KgCO2e | 7369336 | |||
| Over all carbon foot print / year | Ton | 7369 | ||||
| Total population (avg) | 7000 | |||||
| Carbon Foot Print per capita in Ton | 1.05 | |||||
| National average per capita | 1.58 Ton/Capita/Year |
| Actual CO2 emission | 1.05 Ton/Capita/Year |
| % of CO2 emission – on National avg. | 66.63% |
| % of CO2 reduced from National avg. | 33.37% |
CARBON OFFSETTING
| Total Carbon Emission : 7369 tons/year | ||||
| Classification of Green Areas | Area | Unit | CO2 (avg.) absorption rate t/year | Total CO2 absorption ton/year |
| Area of Tree – ref Google Map | 2 | Acre | 160 | 336 |
| Lawn & plant area | 14 | Acre | 15 | 211 |
| Beema Bamboo | 2.5 | Acre | 80 | 200 |
| Total green area in acre | 9 | Acre | ||
| Total CO2 Absorption | 747 | |||
| % of CO2 offset within the campus | 10.13% | |||
| % of Green Area | 37.86% |
10 % of Carbon foot print is offset by the above environment – friendly measures in campus.
Calculation:
Carbon Offsetting
Total trees green area – 19 Acres
Total Co2 absorption ton/year – 747 tones
Over all carbon foot print/year (Co2 Emission) – 7369 tones
% of Co2 → offsetting within campus
(747 / 7369 X 100) – 10.13%
Bal: 90% to be offset by planting more trees or trading
% of Linear area (19/50 Acres – carbon foot print) – 38%
Carbon Footprint
Total Co2 Emission per year: Kg – 7369336
Over all carbon foot print / year = 7369336
———— – 7369 tones
1000
Total Population (Avg.) – 7000 (students)
Carbon foot print per Capita in Ton = 7369
——– – 1.05
7000
National Avg. per emission – 1.58 / ton / capita / year
Actual Co2 Emission – 1.05 / ton / capita / year
% of Co2 Emission on National Avg. 1.05
—— X 100 – 66.46%
1.58
% of Co2 reduced from National Avg. 100 – 66.46 – 33.54%
SUPPORT TO GOVERNMENT
Inauguration of “Continuous Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Station (CAAQMS)”

Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board & B.S.Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science & Technology Jointly organized and implemented Continuous Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Station (CAAQMS) in the Campus on 28th October 2020.
The Project was inaugurated by Mr. D.Vasudevan, District Environmental Engineer, Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board and Dr. A.Peer Mohamed, Vice Chancellor. Dr. A.Azad, Registrar, Alhaj V.N.A.Jalal, Senior General Manager, Dr. N.Raja Hussain, Deputy Registrar took part in the inauguration.


Renewable Energy – Solar Power Plants
In modern times, the generation of energy is disproportionate to the demand. Therefore, conservation of energy is a pivotal requirement to meet the demand. The minimal use of energy and finding alternative sources ensures its continuous supply for a long time. With this aspect in mind, energy conservation is done by using the most modern techniques.
As a part of its ‘Green Campus’ initiative, our Institution has set up a 550 kWp grid tied Rooftop Solar PV Power Plant on its academic buildings. The plant is located in the vacant roof space of various buildings.
The outputs from all the plants are connected to the institute grid through local AC distribution boards. This output can be used anywhere in the campus. Available diesel generator set is being used to create the local grid during load shedding.
If a Solar Power Plant is connected with DG SET and the power consumption of connected Load is lower than the power generated by solar power plant, then the excess of power generated by solar power plant will reverse back to DG SET and this will lead to permanent damage of DG SET. Zero Export device has been installed to limit the surplus amount of solar power that their systems export to the DG SET.

INSTALLED ROOFTOP SOLAR PV POWER PLANT
Installed 550 kWp Rooftop solar plant shares all the power generated with DG set to reduce its dependence on diesel as fuel.
Most recently, a 100 kWp rooftop plant is installed in New Architecture Block and CIIC Block. This installation shall run in parallel to the existing 550 kWp solar plants.

B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology undertakes initiatives to obtain energy from various natural resources. The Institute is pioneer in establishing renewable energy sources to meet the energy requirement of the campus.
Three Roof top solar power plants of total capacity of 650 KWp (against the sanctioned demand of 1200 KW) are installed in our campus.
SOLAR PANEL INSTALLED AT ROOF TOP IN VARIOUS BUILDINGS
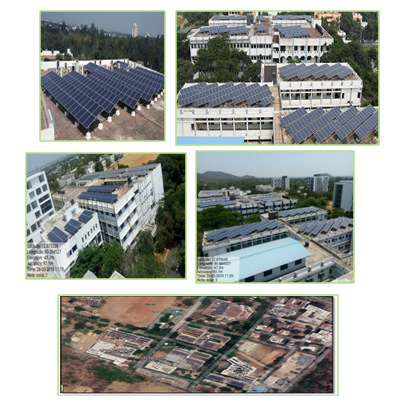

Google Satellite Map View
RENEWABLE ENERGY – SOLAR WATER HEATERS
Installed total capacity of 36,500 liters. This is equivalent to 365 Nos electric geysers of 2kW capacities. The power saving is estimated to be around 24 Lacs per annum.

RENEWABLE ENERGY – SOLAR STREET LIGHT
Installed towards staff quarters to Men’s hostel road and Architecture block area. This project was done by our III yr. EEE students along with our Estate electrical dept. team.

Oxyzone Campus – Beema Bamboo Plantation
Planted bamboo saplings for 5000 run area throughout our compound to absorb dust, CO2 and to release more oxygen and to create pollution free environment. In future, Central bus stand will produce lot of pollution inside our campus, by planting bamboo, our campus become dust free zone with good oxygen supply. Our Institute is provided first OXYZONE inside our campus. Beema Bamboo Plants 2000 Nos Planted in whole campus for CO2 reduction.
Oxy Park

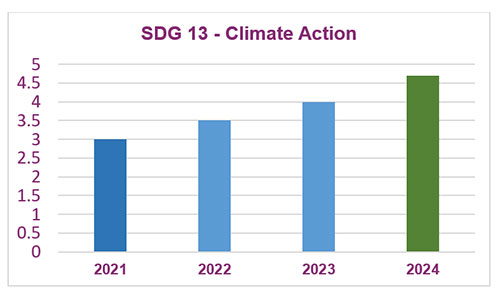
SDG13: Climate Action
| 4 to 5 | There is significant progress in effective implementation compared to the previous year |
| 3 to 4 | The necessary processes/activities (Low-carbon energy use, Environmental education measures, Commitment to carbon neutral campus) have been implemented |
| 2 to 3 | There is an explicit plan to address the ‘Climate Action’ and necessitated processes have been initiated |
| 1 to 2 | There is an understanding and willingness to contribute effectively for achieving the UN targets of SDG 13 |
| 0 to 1 | There is no/partial willingness and plan to contribute for achieving the UN targets of SDG 13 Climate Action |



