Crescent Sustainability Initiatives
CLEAN WATER AND SANITATION (SDG 6)
B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology has implemented measures to prevent polluted water from entering the water system, specifically targeting pollution resulting from accidents and incidents.
A. DESCRIPTION OF THE DIAGRAM (FIGURE VI – 1):
The provided diagram outlines the water management infrastructure of the B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, showcasing various types of water lines across the campus.
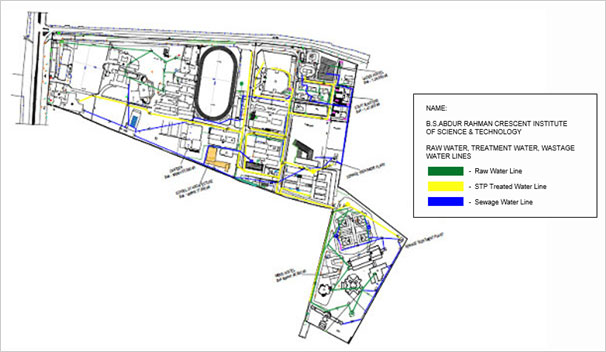
Figure VI (3.2) – 1: Existing water supply and drainage pipeline layout with width of drains, invert levels & disposal to prevent polluted water from entering the water system
OVERALL LAYOUT
- The map depicts the campus layout, highlighting key buildings and areas. Various color-coded lines represent different water types and their management systems.
2. COLOR-CODED SYSTEMS
- Raw Water Lines (Green): These lines indicate the pathways through which untreated or source water is supplied to the campus. This water is typically drawn from local sources before any treatment process.
- STP Treated Water Lines (Yellow): The yellow lines represent water undergoing treatment through the Sewage Treatment Plant (STP). This recycled water is suitable for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and cooling processes, reflecting the institution’s sustainability efforts.
- Sewage Water Lines (Blue): The blue lines illustrate the sewage discharge routes, showing how wastewater is collected and directed to the treatment plant for processing. This ensures effective sanitation and environmental management.
3. INFRASTRUCTURE ELEMENTS
- The diagram highlights important infrastructure components, such as the Sewage Treatment Plant (STP), water tanks, and other critical facilities. These components are strategically located to optimize water flow and management across the campus.
4. OVERALL FUNCTIONALITY
- The design emphasizes an integrated approach to water management, showcasing how raw water is sourced, treated, and utilized effectively while also addressing sewage disposal. This organized system reflects the institute’s commitment to sustainability and efficient resource use.
The map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the water management framework at B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology. By clearly outlining the raw water, treated water, and sewage systems, it provides insight into the institution’s initiatives for maintaining water quality and promoting environmental sustainability on campus.
B. LAYOUT OF PIPELINES FOR WATER AND WASTEWATER (FIGURE VI – 2)
- PLUMBING AND WATER COLLECTION SYSTEMS
- The institute has established a meticulously planned plumbing facility for the collection and treatment of water. This includes the transportation of water from wells to treatment units, ensuring that pipes are laid at suitable gradients to facilitate safe water transport.
- Regular inspections are conducted to check for leaks in the water pipelines, and immediate replacements are made in case of breakages due to accidents. This proactive maintenance helps prevent polluted water from entering the water system.
- SEPARATE SEWER SYSTEMS
- Wastewater is collected through separate sewer pipelines, which are equipped with sufficient manholes for easy inspection. This segregation ensures that wastewater does not mix with potable water sources, thereby reducing the risk of contamination.
- IDENTIFICATION AND MARKING OF PIPELINES
- The institute employs a colour-coded system for easy identification of water and sewer lines:
- Green: Raw water from wells
- Blue: Treated water from the Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) used for toilet flushing
- This clear marking helps prevent accidental cross-connections that could lead to pollution.
- The institute employs a colour-coded system for easy identification of water and sewer lines:

Figure VI (3.2) – 2: Layout of pipelines for water and wastewater – Geo-tagged photographs
C. SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT PRACTICES (FIGURE VI – 3)
- PREVENTIVE MEASURES AGAINST POLLUTION
- The institute has implemented robust solid waste management practices to prevent water pollution caused by improper waste disposal. Key measures include:
- Segregation of Garbage: Garbage is segregated at entry points, particularly from high-traffic areas like hostels and canteens, to minimize contamination risks.
- Minimization of Waste: Efforts are made to reduce the amount of waste, particularly plastics, that could clog pipelines and affect water quality.
- Regular Clearing of Dumping Yards: Frequent disposal of accumulated waste from dumping yards prevents overflow and potential leaching into the water system.
- The institute has implemented robust solid waste management practices to prevent water pollution caused by improper waste disposal. Key measures include:
- SEWER MANAGEMENT
- The sewer connections to the old biogas plant have been redirected to the STP, ensuring that there is no mixing of sewer and rainwater, which could lead to contamination.
- BOUNDARY MANAGEMENT
- Measures have been taken to close any holes along the boundary of the institute that could contribute to water seepage from neighbouring areas, further protecting the water system from external pollution sources.
- EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS
- The institute has additional raw water storage tanks that can be utilized during emergencies, ensuring a reliable supply of clean water and reducing the risk of contamination during unforeseen incidents.


Figure VI (3.2) – 3 : Geo-tagged photographs showing the Collection of Solid Waste, Segregation of Solid Waste, Recovery of Recyclable and Windrow Formation and Rotation
Water Management and Reuse Policy
Issue: 04; Revised on 2023
| Policy Created on | July 2009 |
| 1st Revision amended on | IQAC Meeting held on 27th October 2017 |
| 2nd Revision amended on | IQAC Meeting held on 31st March 2021 |
| 3rd Revision amended on | IQAC Meeting held on 16th June 2023 |
6.1 STATEMENT OF POLICY
The B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology is committed to achieving the following objectives in alignment with Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) – Clean Water and Sanitation:
- a) Ensure universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all stakeholders.
- b) Provide adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all, with special attention to the needs of women, girls, and vulnerable groups.
- c) Improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping, and minimizing the release of hazardous chemicals and materials.
- d) Halve the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increase recycling and safe reuse globally.
- e) Substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and freshwater supply to address water scarcity.
- f) Implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including transboundary cooperation as appropriate.
- g) Protect and restore water-related ecosystems, including mountains, forests, wetlands, rivers, aquifers, and lakes.
- h) Expand international cooperation and capacity-building support to developing countries in water- and sanitation-related activities and programs.
- i) Support and strengthen the participation of local communities in improving water and sanitation management.
6.2 REASON FOR THIS POLICY
The policy aims to provide all stakeholders with adequate water supply, sanitation, and hygiene. It emphasises maximising the collection and treatment of sewage generated and the reuse of treated wastewater sustainably, thereby reducing dependency on freshwater resources. The policy promotes treating wastewater as an economic resource.
6.3 RESPONSIBILITIES
6.3.1 Policy Principles
- a) The campus shall provide adequate water supply and maximize water reuse by adhering to the following principles:
- Equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all stakeholders.
- Access to adequate sanitation and hygiene, ending open defecation, with special attention to vulnerable groups.
- Calculation of water usage per person (students, staff, and faculty) annually.
- Improving water quality by reducing pollution and increasing recycling and safe reuse.
- Utilization of recycled/treated wastewater for beneficial purposes, such as irrigation and toilet flushing.
- Implementation of integrated water resources management at all levels.
- Protection and restoration of water-related ecosystems on campus.
- Expansion of rainwater harvesting initiatives.
- Collaboration with government, NGOs, and industries in water-related activities.
- Support for student and staff participation in water management.
6.4.1 Water Reuse Policy Objectives
- Establish a comprehensive policy to maximize water reuse across the university.
- Ensure that all new buildings adhere to water-conscious building standards that facilitate water reuse.
- Implement systems for tracking and measuring water consumption and reuse.
6.4.2 Water Reuse
- Water Reuse Policy: maximise water reuse across the university.
- Water Reuse Measurement: Measure water reuse across the university.
6.5 DISSEMINATION OF POLICY
- a) Display signage promoting water use efficiency across the campus.
- b) Conduct awareness programs at regular intervals to increase water-use efficiency.
- c) Post the policy on the Institute’s website and update it as necessary.
6.6 ENFORCEMENT OF POLICY
- a) The Director (Planning & Development) and Deputy Director monitor compliance and address breaches.
- b) Awareness of the policy among students, staff, and visitors is essential.
- c) Breaches may lead to disciplinary action as per the Institute’s code of conduct.
REGISTRAR


